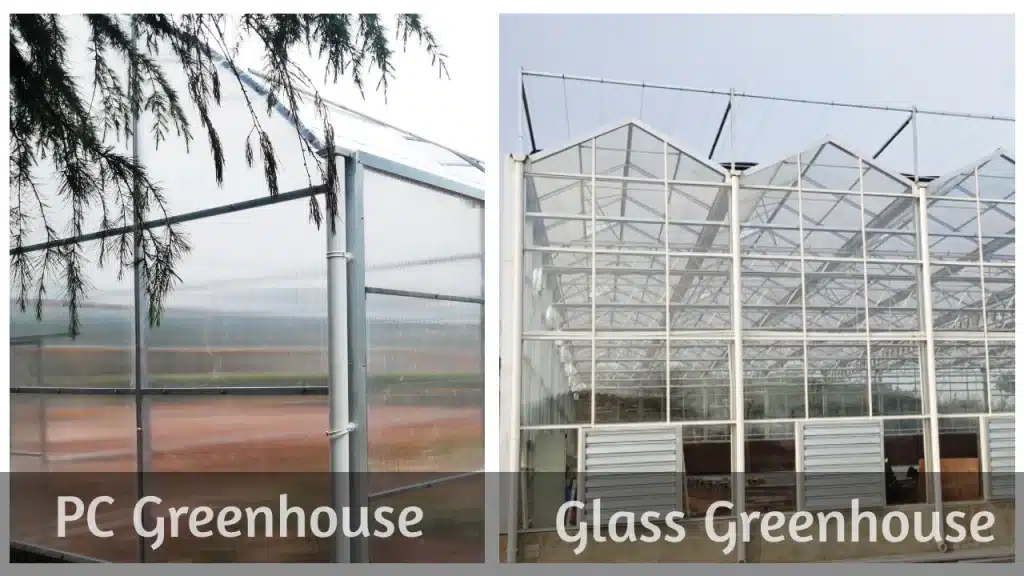
In the realm of contemporary smart agriculture, leveraging commercial greenhouses has become an indispensable technological approach. These greenhouses present a controlled and stable setting for plant cultivation, making it possible to optimize growth conditions, augment yield, and broaden the area of cultivation. In order to fulfill these goals, selecting the most suitable greenhouse covering material is of paramount importance.
Glass and Polycarbonate stand as two of the most widely used materials in today’s greenhouse market, each displaying unique attributes. The choice between them, however, involves a comprehensive evaluation from various angles.
This article will delve into a detailed analysis of the features of these two materials. Furthermore, it will offer a comparison between Polycarbonate and Glass greenhouses across eight different aspects, which will serve to provide clarity on whether Polycarbonate is indeed a better choice than glass for greenhouses.
Overview: Polycarbonate vs Glass Greenhouse
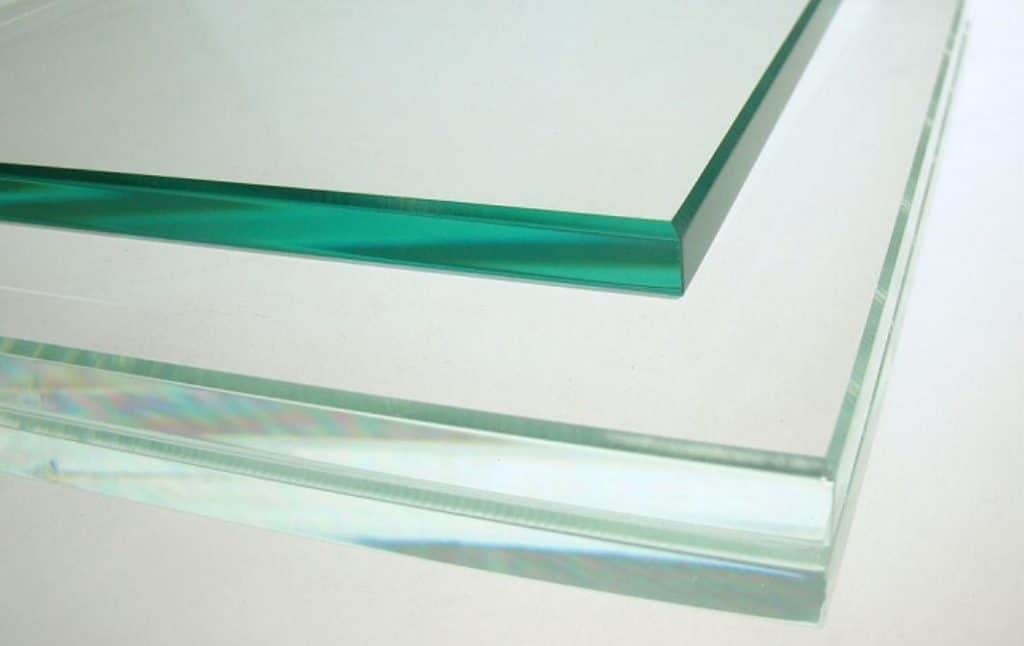

As the name implies, a glass greenhouse is a type of greenhouse that uses glass as its covering material. Owing to its exceptional transparency and weather resistance, glass was among the first materials to be extensively utilized in greenhouse construction. While it provides a degree of insulation, its substantial weight leads to higher installation and maintenance costs.
Polycarbonate, or polycarbonate sheets, is a novel building material. Its high transparency, lightweight, strong impact resistance, and superior insulation properties have led to its growing popularity in greenhouse construction. Particularly appreciated is the anti-fogging property of Polycarbonate, which ensures a good light transmission rate inside the greenhouse even under high humidity conditions.
Here’s a quick comparison table of the two different types of greenhouses:
| Properties | Glass Greenhouse | Polycarbonate Greenhouse |
| Light Transmission | High (Over 90%) | Moderate (80%-90%) |
| Insulation Performance | Moderate | High |
| Impact Resistance | Low | High |
| Foundation Design and Load-Bearing | High | Lower |
| Special Installation Aluminum Profile | Heavy, strong load-bearing | Lighter, slightly weaker load-bearing |
| Lifespan | Longer | 5-15 years |
| Initial Investment and Maintenance Cost | High | Moderate |
| Wind Resistance | Average | High |
| Investment Returns | Possibly higher in the long term | Possibly higher in the short term |
Glass vs Polycarbonate Greenhouses: 8 Aspects In-depth Comparison
Here we delve into a detailed comparison and explanation of Glass and Polycarbonate greenhouses across 8 important aspects in commercial greenhouse construction. We hope you find it useful.
1. Light Transmission
Both glass and polycarbonate must allow sufficient light to pass through to ensure plants can perform photosynthesis. Theoretically, glass has a slightly higher light transmission rate, reaching over 90%, while polycarbonate can also reach up to 89%, rendering their performance fairly comparable in this aspect.
However, simply comparing light transmission rates cannot fully evaluate the performance of the materials in actual use. Given that the humidity inside a greenhouse is typically higher than outside, moisture in the air condenses into droplets on the greenhouse roof. These droplets obstruct the light, reducing the actual light transmission rate.
Polycarbonate greenhouse coverings, with their unique anti-drip design, effectively reduce droplet formation, allowing the actual light transmission rate to be close to the theoretical value. For glass greenhouses, which lack an anti-drip feature, the actual light transmission rate often falls below the theoretical value. Therefore, from the perspective of actual light transmission, polycarbonate may outperform glass.
2. Load-Bearing and Installation Difficulty
When selecting covering materials, their weight and load-bearing capacity need to be considered, as they directly impact the design of the greenhouse structure and the installation difficulty. Glass weighs significantly more than polycarbonate, meaning that glass greenhouses require more robust foundation design and frame load-bearing, necessitating higher standard steel for support. Conversely, the lightweight polycarbonate places less demand on the greenhouse foundation and frame load-bearing, making it easier to install.

This, however, does not suggest that polycarbonate’s weather resistance and durability are necessarily inferior to glass. In fact, polycarbonate exhibits excellent impact resistance and weathering characteristics.
3. Supporting Aluminum Profiles
The installation of covering materials requires matching aluminum profiles for fixation. The aluminum profiles needed for glass and polycarbonate greenhouses are different. Glass greenhouses require thicker profiles that offer stronger load-bearing capabilities, thereby increasing the quantity used and driving up costs. On the other hand, polycarbonate greenhouses require thinner profiles, which bear less weight, but are more cost-effective due to lower material and installation costs.
4. Ancillary Facilities
Different covering materials have different requirements for ancillary facilities. While there are differences in the foundational design, structural load-bearing capacity, and aluminum profile installations between glass and polycarbonate greenhouses, most other components are interchangeable.
This includes external shading, automatic roof windows, electric interior shading, fans, and humid curtains. These facilities are designed to improve the internal environment of the greenhouse and provide optimal growing conditions. This design flexibility gives more choices to different types of greenhouses, making greenhouse construction more versatile.
5. Lifespan and Maintenance Requirements
The lifespan and maintenance requirements are another critical factor when choosing covering materials. Glass greenhouses have a longer lifespan, but the glass is prone to scratching and damage, leading to higher maintenance costs.
The lifespan of polycarbonate greenhouses varies depending on the specific product, typically ranging from 3-5 years to 10 years. However, high-quality polycarbonate, such as those with a UV-resistant co-extrusion layer, can effectively resist UV radiation, extending the sheet’s life to ten years under warranty, with an effective usage lifespan that can reach up to 20 years.
6. Return on Investment for Greenhouses
The return on investment is another important factor when choosing the covering material for agricultural greenhouses. While the initial investment for glass greenhouses might be higher, their longer lifespan and stable performance may yield greater long-term returns. However, due to the lower installation and maintenance costs of polycarbonate, its short-term return on investment might be higher.
7. Influence of Site and Climatic Conditions
The performance of different covering materials may vary based on specific site and climatic conditions. For example, in areas with high winds, polycarbonate greenhouses may have an advantage over glass greenhouses due to their better wind resistance. In areas with abundant sunlight, glass greenhouses might perform better because of their higher light transmittance.
8. Greenhouse Selection Based on Specific Crop Needs
Different crops may require different light, temperature, and humidity conditions, so these factors need to be considered when choosing a covering material. For instance, crops with high light requirements might be better suited to glass greenhouses that have a higher light transmittance. In contrast, crops with high temperature and humidity control need might be better suited to polycarbonate greenhouses, which offer superior insulation and anti-drip properties.
FAQs
1. What are the disadvantages of a glass greenhouse?
Glass greenhouses, although having excellent light transmission and weather resistance, do have several drawbacks.
Firstly, they are typically heavier and more delicate, leading to higher installation and maintenance costs. The weight of the glass also demands a sturdier and thus costlier framework for support. Additionally, they lack an anti-condensation feature, which can reduce the actual light transmission rate under high humidity conditions within the greenhouse.
2. What are the disadvantages of polycarbonate greenhouses?
While polycarbonate greenhouses offer many advantages, such as lightweight, high-impact resistance, and superior insulation properties, they also have a few downsides.
The lifespan of a polycarbonate greenhouse can be shorter than that of a glass greenhouse, typically ranging between 5-15 years depending on the quality. The light transmission rate of polycarbonate is slightly less than that of glass. Also, while they are easier to install and modify, the lighter-weight structure might be less stable in extreme weather conditions.
3. What is the best material for a commercial greenhouse in winter?
When considering the best material for a greenhouse in winter, polycarbonate stands out. This material offers superior insulation than glass due to its double-wall structure that traps air, reducing heat loss and keeping the greenhouse warm. It’s also more durable and impact-resistant, making it ideal for areas with heavy snowfall or wind.
However, the specific needs of the plants and the local climate are important factors. While polycarbonate is generally favorable, some plants may benefit from the slightly higher light transmission of a glass greenhouse. It’s best to assess your unique situation and consult with a greenhouse expert if needed.
Conclusion
When considering factors like adaptability and cost-effectiveness, most large-scale plantations engaged in smart agriculture today lean towards choosing polycarbonate greenhouses. Furthermore, the superior weather resistance, impact resistance, and insulation properties of polycarbonate make it adaptable to a variety of climatic conditions, which is another reason people choose it. Although the lifespan of polycarbonate might be somewhat shorter than glass, its lower initial investment, maintenance costs, and ease of expansion and modification make it a more economical choice.
If you are considering building your commercial greenhouse and need corresponding solutions, please contact our INSONGREEN team in China. Our geographical location enables us to provide highly cost-effective solutions for large-scale commercial greenhouses. Finally, thank you for reading. If you have any questions about the content of this article, please get in touch with us.





