Thinking of starting a professional or commercial greenhouse project, but unsure where to begin? With so many greenhouse structures, materials, and technologies out there, choosing the right type can feel overwhelming. Whether you’re growing vegetables, flowers, fruit trees, or even exploring aquaculture or livestock production, your greenhouse setup can make or break your success.
Don’t Miss: Greenhouse Farming vs. Traditional Farming
In this guide, we at INSONGREEN break down over 20 different types of commercial greenhouses by use, structure, roof type, covering materials, and technology to help you find the perfect fit for your goals and budget.
Types of Commercial Greenhouses You Can Choose from
Commercial greenhouses vary widely because they are made with different technologies, require different amounts of money to set up, and serve different purposes. They are often grouped based on what they are made of, their design, their function, and how technologically advanced they are.
Next, we’ll look at greenhouses from four angles: their use, design and layout, the materials they’re covered with, and their technological features.
1. Classification by Primary Use
Before choosing structural and material features, it’s essential to define the primary purpose of your greenhouse. Whether you’re growing crops, cultivating flowers, or using it for exhibitions, this intended use directly influences the design, environmental controls, and overall cost. In this section, we’ll explore six common types of agricultural greenhouses based on their main function.
1)Nursery Greenhouse
Nursery greenhouses are all about starting plant life. They are specifically designed to help seeds sprout and young plants grow. These agricultural greenhouses create the perfect conditions for seeds to germinate and for young seedlings to thrive during their critical early stages.
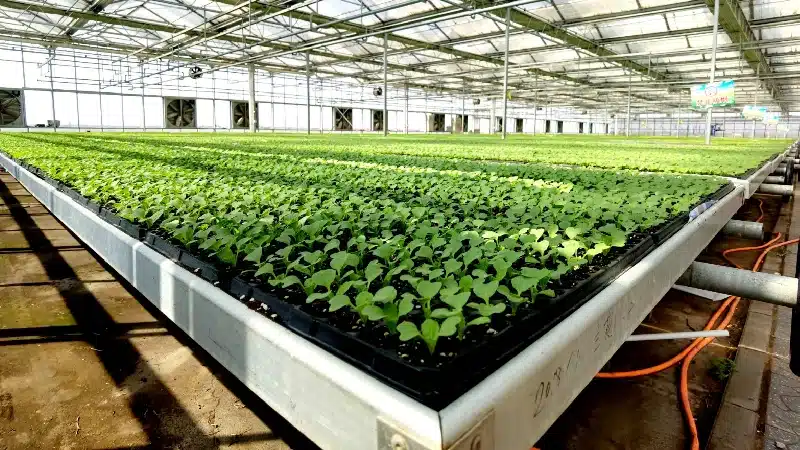

2)Vegetable Greenhouse
As one of the most common types of agricultural greenhouses, a vegetable greenhouse is specifically designed for cultivating vegetables in a controlled environment. By managing temperature, humidity, and light, this setup increases yields, extends the growing season, and enables off-season production. It also protects crops from frost, heavy rain, and extreme heat, while helping to manage pests and diseases more effectively. The ultimate goal is to ensure a consistent supply of high-quality vegetables throughout the year, keeping pace with market demand.
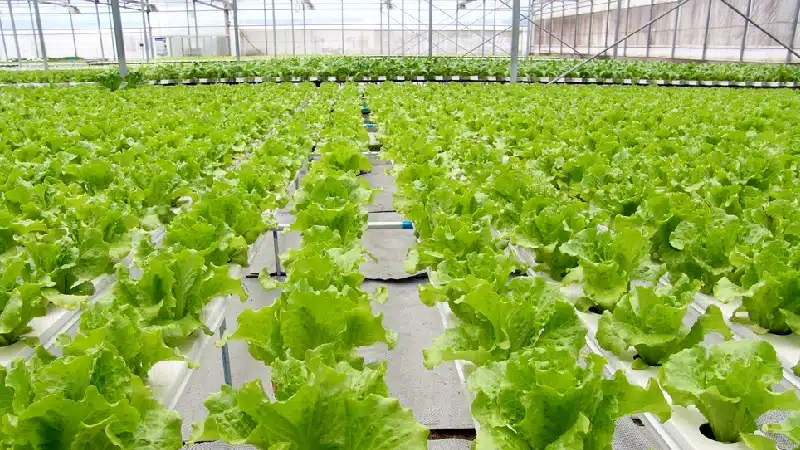

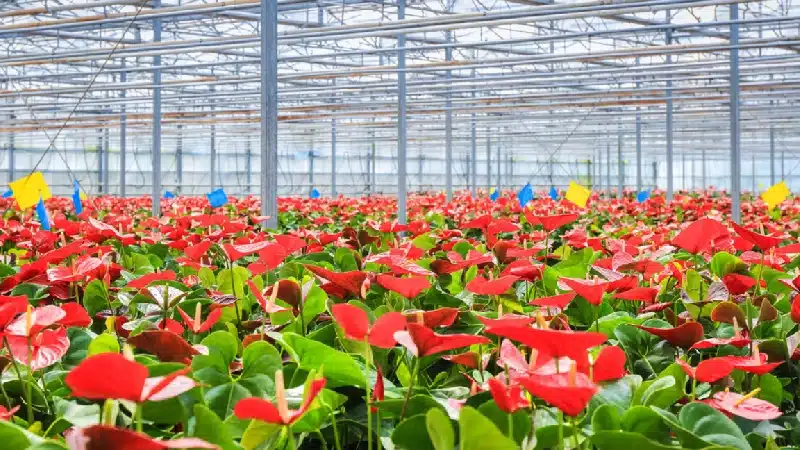
3)Floriculture Greenhouse
Floriculture Greenhouses are dedicated to the cultivation and care of flowering plants. These structures provide a protected environment that shields plants from harsh weather and ensures optimal growth conditions. By controlling temperature, humidity, lighting, and ventilation, floral greenhouses support healthy flower development, prolong the blooming period, or even trigger earlier blooming.

4)Fruit Tree Greenhouse
Fruit tree greenhouses are designed to cultivate fruit trees under artificially controlled environmental conditions. These greenhouses adjust temperature, humidity, and lighting to create the perfect setting for fruit trees to flourish. They enable faster growth, prolong the fruit-bearing season, or allow for off-season fruit production. This capability is particularly valuable for producing fruit all year round or in regions with climates that typically do not support certain fruit trees.
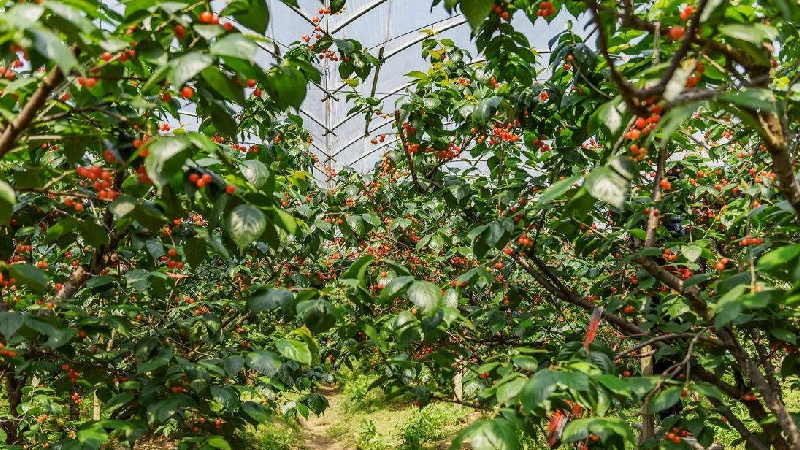

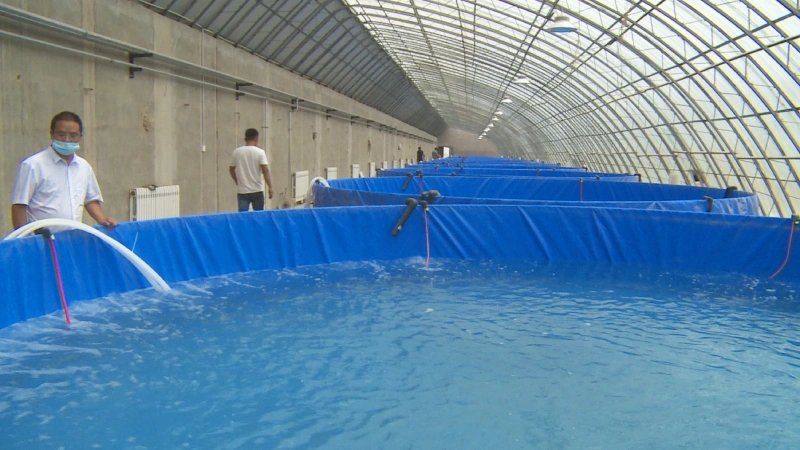
5)Aquaculture Greenhouse
Aquaculture greenhouses represent a novel approach by merging greenhouse technology with fish farming. These greenhouses use their structures to control the environment, optimizing conditions for the growth of aquatic species such as fish, crustaceans, and shellfish. This innovative model blends traditional plant greenhouse techniques with modern aquaculture practices, aiming to boost production efficiency and minimize environmental impacts while ensuring high yields.

6)Livestock Greenhouse
Livestock overwintering greenhouses are built specifically to shelter livestock during the harsh winter months. These greenhouses offer a warm and stable environment that helps protect animals from the cold, minimizing the impact on their health and productivity. This approach has become particularly popular in China.
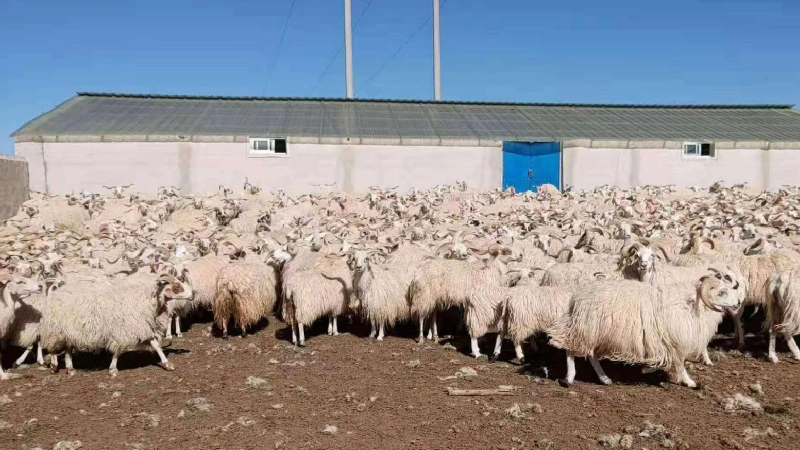

For instance, in Rixie Village, warm sheds for livestock have been constructed using funds allocated for poverty alleviation from Shanghai. These facilities are crucial in ensuring the welfare of the animals throughout the winter, helping them stay healthy and productive even in colder temperatures.
2. Classification by Structural Features
Once you’ve identified your greenhouse’s purpose, the next key consideration is its structure. Each greenhouse structure has its own benefits and trade-offs. It significantly affects how plants are housed, how air and light circulate, and how efficiently internal conditions can be controlled. Generally, commercial greenhouses fall into five categories based on their structure.
1)Single-Span Greenhouse
A single-span greenhouse or freestanding greenhouse is built individually and doesn’t require drainage gutters. Its design allows snow to slide off the roof naturally, preventing excessive weight and potential damage. These greenhouses are often equipped with side windows that can be opened to enhance ventilation, making them particularly effective at keeping cool during hot summers.
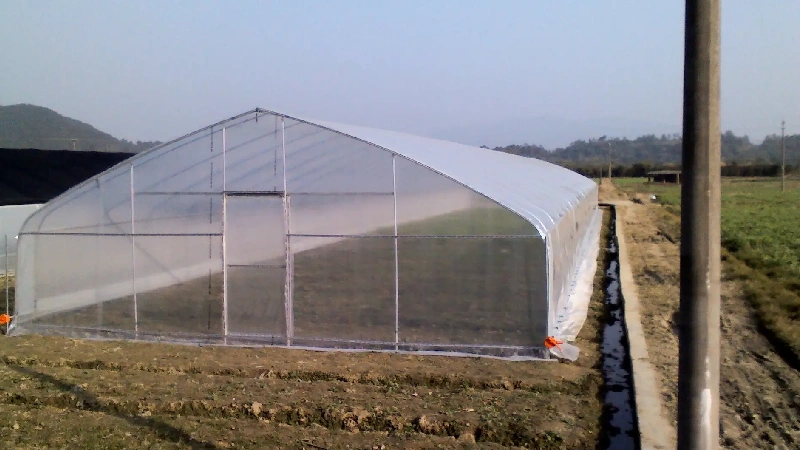

2)Multi-Span Greenhouse
Multi-span greenhouses consist of two or more single-span greenhouses connected at the eaves. The walls between these connected units are removed, and gutters are added, creating a continuous, unified structure. This type allows for larger, more controlled environments ideal for extensive agricultural operations. Several types of multi-span greenhouses are based on the materials used, such as multi-span glass greenhouses, multi-span polycarbonate greenhouses, and multi-span film greenhouses.
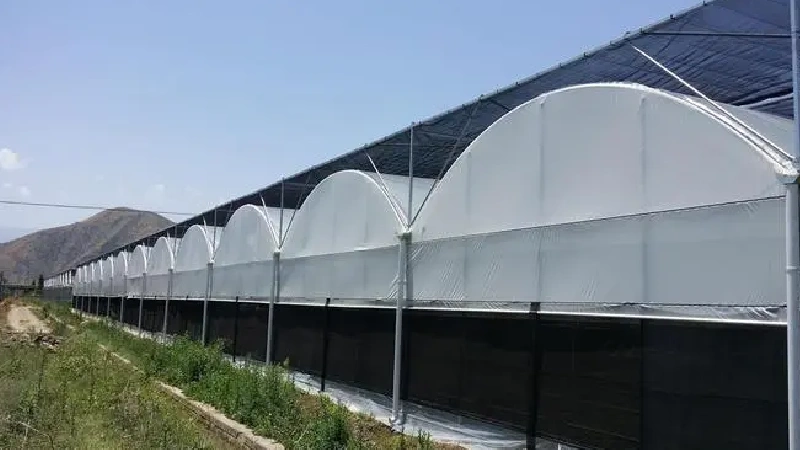

3)Even-Span Greenhouse
An even-span greenhouse features two symmetrical roof slopes extending from a central ridge, forming a balanced A-frame structure. This type is common in both single-span and multi-span configurations. Its symmetrical design allows for uniform light distribution, efficient snow shedding, and good structural stability. In large-scale production, even-span and multi-span structures are often combined or scaled up to form industrial greenhouses that meet higher yield demands.
4)Chinese Greenhouse (Special Structure)
Special structure greenhouses are designed with unique features to meet specific agricultural needs or to maximize efficiency in particular climates. Examples include the solar greenhouse, the Yin-Yang greenhouse, and the Venlo-type greenhouse.
Passive Solar Greenhouse
Also known as Chinese-style greenhouses or Chinese cold frames, these structures are built with sidewalls, a rear maintenance wall, a support framework, and typically a film covering. They are predominantly found in northern China, where they leverage solar energy to maintain warmth. The rear wall absorbs sunlight, storing and releasing heat to keep the interior warm enough for crops, usually without the need for additional heating except in extremely cold conditions or for special crops.
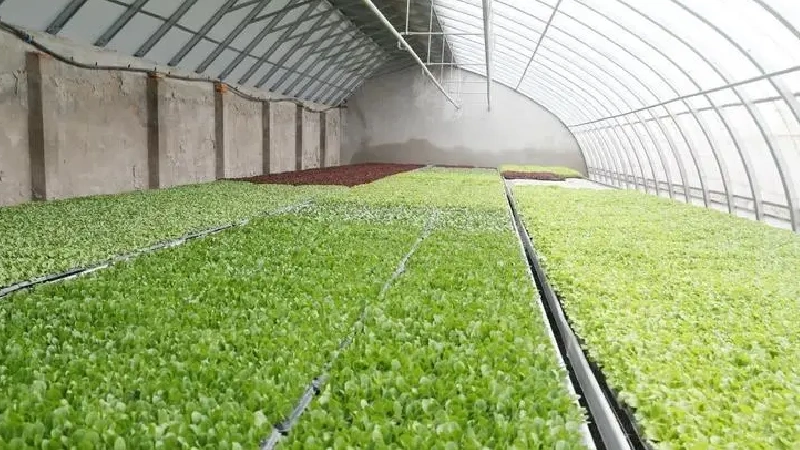

Yin-Yang Greenhouse
The Yin-Yang greenhouse is an innovative variation of the Chinese passive solar greenhouse. Its name reflects the design philosophy: a sloped, south-facing ‘Yang (阴)’ side captures maximum sunlight for heat gain, while the north-facing ‘Yin (阳)’ side provides enhanced insulation to minimize heat loss. This balanced thermal structure creates two distinct zones within the same greenhouse, making it particularly effective for cultivating mushrooms and shade-loving crops that require lower light intensity. The design is especially well-suited for regions with significant temperature fluctuations between day and night.

5)Lean-To Greenhouse
Lean-to greenhouses are built against the wall of an existing structure, with the roof sloping away to create a compact, cost-saving layout. While economical and space-efficient, they offer limited growing area, restricted airflow, and uneven light distribution—factors that make them less suitable for large-scale commercial use. As a result, lean-to designs are more commonly seen in backyards, educational facilities, or as seasonal propagation houses.
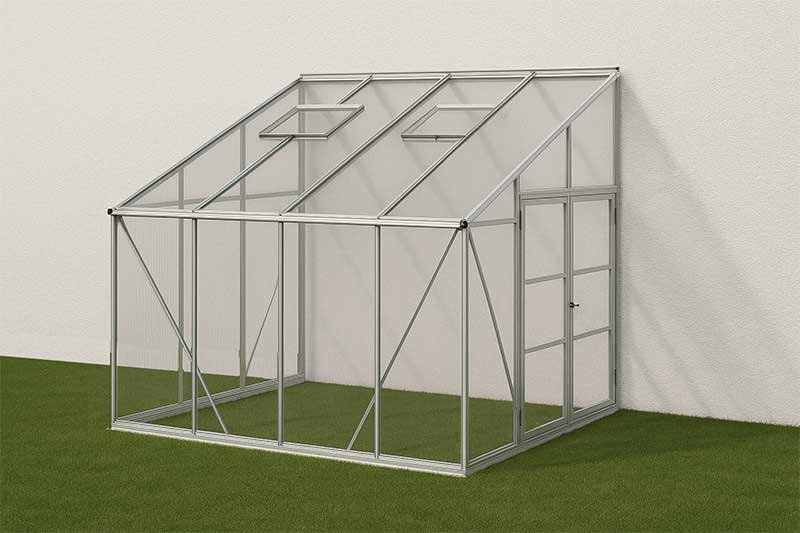

Interestingly, the basic lean-to concept also appears in China’s passive solar greenhouses. However, unlike traditional Western lean-to structures, the Chinese version features a dedicated, thick rear wall specifically built for thermal storage, not for structural reuse. This distinction has enabled Chinese-style greenhouses to evolve into a highly functional, stand-alone design for winter vegetable production in cold regions.
3. Classification by Roof Types
Beyond the overall structure of a greenhouse, the roof design plays a crucial role in its overall performance. Even greenhouses with similar frames can vary greatly in light penetration, ventilation, drainage, and insulation depending on the roof type. The shape and features of the roof not only influence the internal environment but also determine how well the greenhouse adapts to specific crops and climate conditions. Based on roof design, greenhouses can generally be classified into the following types.
1) Venlo Greenhouse
The Venlo greenhouse, originating in the Netherlands, is a hallmark of modern high-tech greenhouses. Its roof features a series of triangular ridges, maximizing sunlight exposure while minimizing shading. The ridge vent system efficiently releases excess heat, making it ideal for crops like tomatoes and flowers that thrive in bright light.
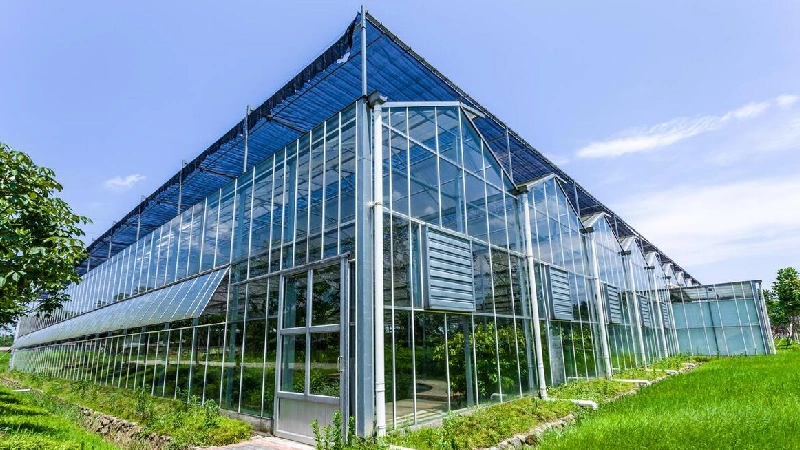

Typically, Venlo greenhouses use materials like glass or polycarbonate panels, which provide excellent light transmission and insulation. These greenhouses are widely used in temperate and cold regions for large-scale commercial cultivation.
2) Dome Greenhouse
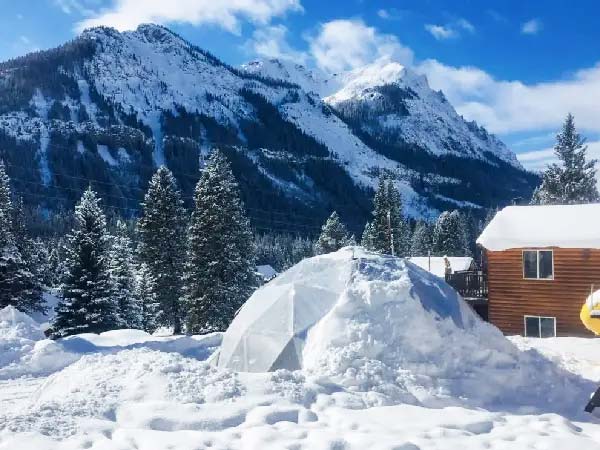

The dome greenhouse is known for its distinctive curved roof, which creates a spherical structure that excels at snow and water drainage. This design also reduces structural stress, which is particularly suitable for areas prone to heavy snowfall or strong winds. Dome-shaped roofs ensure even light distribution throughout the interior, promoting balanced plant growth. Dome greenhouses are commonly used in small-scale farms, backyard gardens, and exhibition spaces, combining functionality with aesthetic appeal.
3) Sawtooth Greenhouse
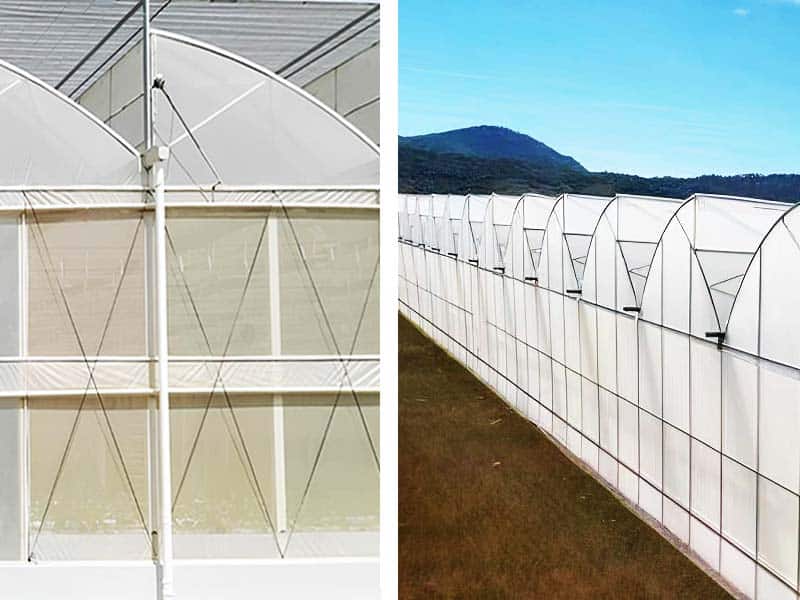

Sawtooth greenhouses, characterized by their wavy roof design, are widely found in tropical and subtropical regions. The sloped roof sections enhance natural ventilation, reducing the reliance on artificial cooling systems and optimizing the internal climate. This design also helps diffuse light evenly across the greenhouse, preventing hotspots.
4) Flat-Roof Greenhouse
Flat-roof greenhouses, with their completely flat-roof design, are less common but serve specific purposes. While their simple structure makes them cost-efficient and easy to construct, poor drainage and water or snow accumulation risk are significant drawbacks. To counter these issues, specialized drainage systems are often employed. Flat-roof greenhouses are typically used in urban settings for rooftop farming or research facilities and for low-height crops requiring limited vertical space.
4. Classification by Covering Materials
After settling on the structure and roof design, one of the most practical—and often budget-driven—decisions comes down to the covering material. Whether you’re aiming for maximum sunlight, better insulation, or longer lifespan, the material you choose will directly affect your greenhouse’s performance and long-term maintenance costs. Most commercial greenhouses use one of three primary covering options: plastic film, glass, or polycarbonate (PC) sheets.
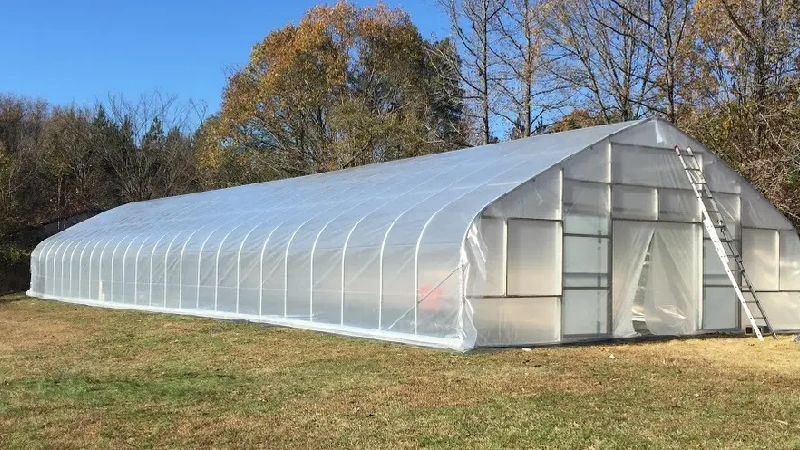
1)Poly Greenhouse
Poly greenhouses, or polyhouses, utilize plastic film as the covering. They are available in both single-span and multi-span designs. These greenhouses are more cost-effective and easier to build and maintain than those made with glass or other more rigid materials. The plastic film helps trap heat efficiently while being light and flexible, although it may need to be replaced more frequently than more durable materials.

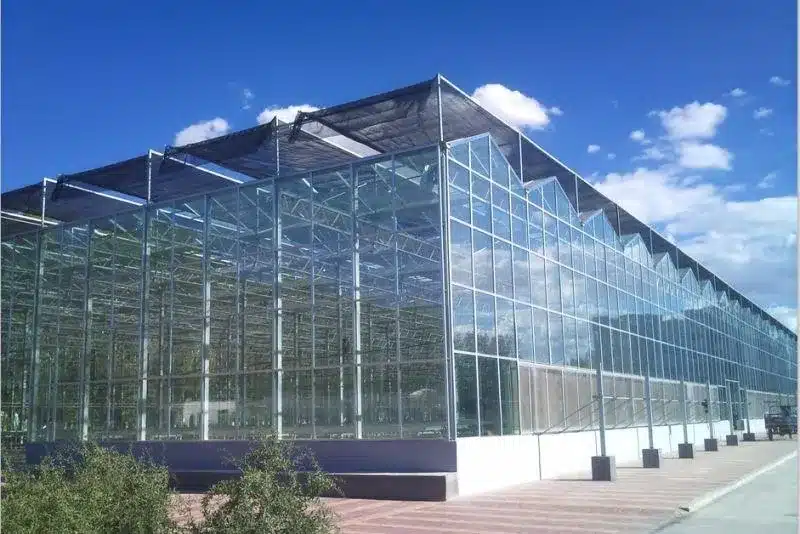
2)Glass Greenhouses
Glass greenhouses use glass as the primary transparent covering material. They are pricier but offer a longer lifespan than poly greenhouses. Glass types can vary from standard clear glass to diffuse glass, which includes options with patterns like pear, fabric, and double velvet. These patterns help diffuse light more evenly throughout the greenhouse, benefiting plant growth by reducing glare and hot spots.

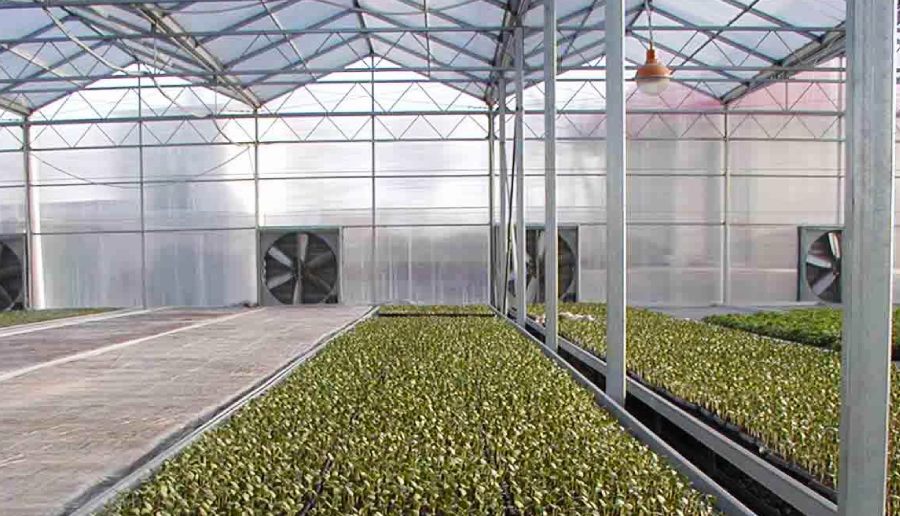
3)Polycarbonate (PC) Greenhouse
Polycarbonate greenhouses, often referred to as PC greenhouses, use double-layer polycarbonate sheets as the primary covering material. These sheets provide excellent thermal insulation due to their low heat conductivity, helping reduce energy costs in both cold and hot climates. Compared to glass, PC panels are lighter, impact-resistant, and flame-retardant, making them a safer and more durable choice for commercial growers. However, the long-term performance of a PC greenhouse depends heavily on material quality—low-grade panels may yellow, become brittle, or lose transparency within a few years. For optimal results, high-quality UV-coated PC sheets are strongly recommended.

5. High-Tech Greenhouse Classifications
High-tech greenhouses go beyond basic functional and material distinctions, incorporating advanced technologies to enhance productivity and environmental safety. These include light, environmentally safe greenhouses, smart greenhouses, and double-layer inflatable film greenhouses.
1)Light Deprivation Greenhouses
Light-deprivation greenhouses, often called blackout greenhouses, are cutting-edge solutions designed to control plants’ photoperiods. By simulating specific light and dark cycles, these greenhouses enable growers to mimic seasonal changes and optimize growth conditions for light-sensitive crops. Equipped with automated blackout curtain systems, they can completely block natural light to manage the growing environment precisely.
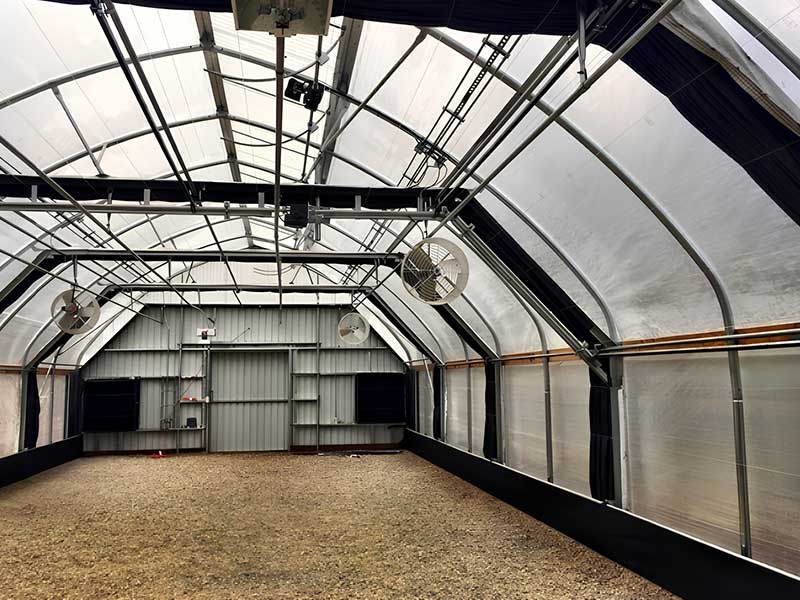

Integrated with advanced control systems, light-deprivation greenhouses support year-round production, enhancing crop quality and increasing yields. These greenhouses are particularly suited for cultivating photoperiod-sensitive plants such as cannabis, chrysanthemums, and other ornamental or medicinal crops.
2)Hydroponic Vertical Greenhouses
Hydroponic vertical greenhouses combine hydroponic systems with vertical farming technologies to maximize production in limited spaces. Using a soil-free method, these greenhouses deliver nutrients directly to plants through a nutrient-rich water solution, eliminating soil-related challenges like pests and diseases. The vertical stacking design allows for high-density planting, making them ideal for urban areas where space is at a premium.
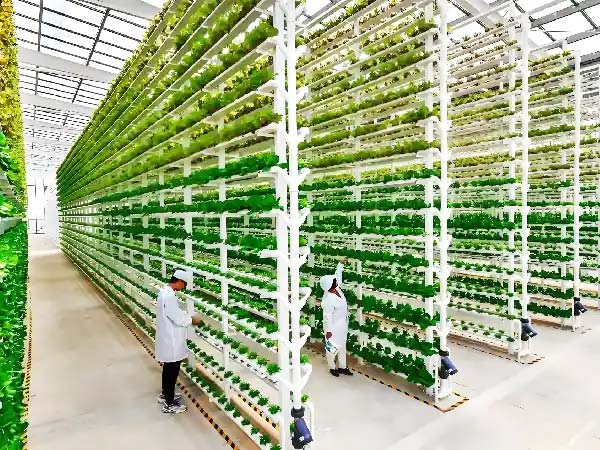

Equipped with smart monitoring systems, they ensure precise control over temperature, humidity, light, and nutrient supply, leading to consistent and efficient crop growth. These greenhouses are particularly beneficial for leafy greens, herbs, and strawberries and are commonly used in urban farming projects, high-demand commercial operations, or regions with limited arable land.
3)Environmentally Safe Greenhouses
These can be subdivided into two main types: physical plant protection greenhouses and environmental control greenhouses.
Physical Plant Protection Greenhouses
These greenhouses rely on physical methods—rather than chemical pesticides—to manage pests and diseases throughout the crop lifecycle. This approach is particularly useful for growers seeking more sustainable or residue-free cultivation methods.
Key techniques include:
- Soil-level protection: Using crop rotation and electrothermal soil barriers to suppress soil-borne pathogens and pests.
- Airborne disease control: Electrostatic fog removal systems filter out fungal spores and airborne contaminants.
- Insect management: Combining colored sticky traps, light-attracting devices, and insect netting to target flying insects effectively.
- Biological reinforcement: Introducing natural predators like ladybugs or predatory mites to support physical controls.
By integrating multiple physical strategies, these greenhouses help maintain a stable, low-risk environment for sensitive or high-value crops.
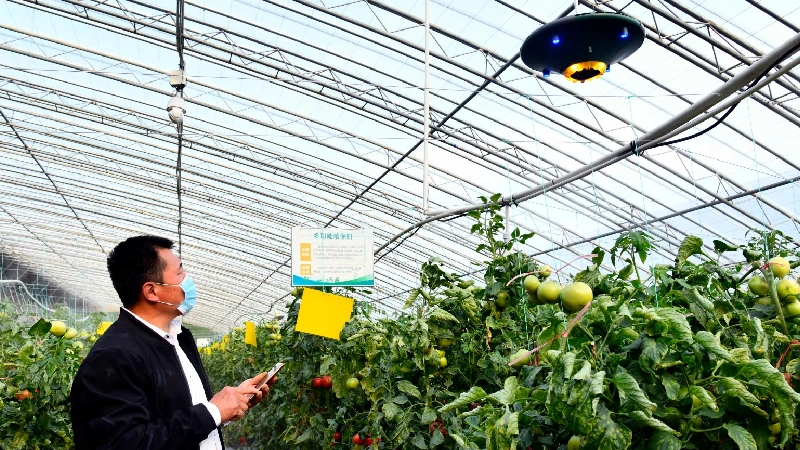

Environmental Control Greenhouses
These greenhouses extend physical plant protection capabilities by regulating temperature, lighting, and carbon dioxide levels to promote pesticide-free growth under various environmental conditions. These greenhouses might feature hot air furnaces, soil heating cables, cooling pads, electrostatic field generators (which also boost photosynthesis in low light), supplemental lighting, and CO2 enrichment systems.
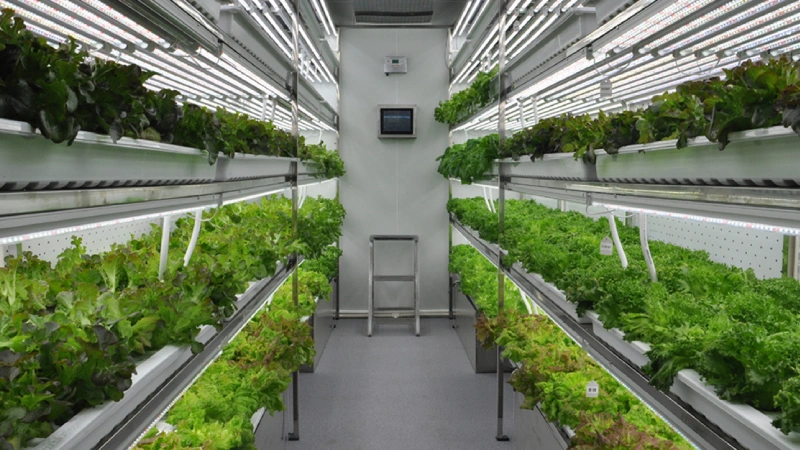

4)Smart Greenhouses
Commonly referred to as modern greenhouses, smart greenhouses are at the forefront of facility agriculture. They incorporate comprehensive environmental control systems that automatically adjust indoor conditions for temperature, light, water, nutrients, and air quality. This sophisticated automation saves significant labor and energy and enhances crop quality and yield.
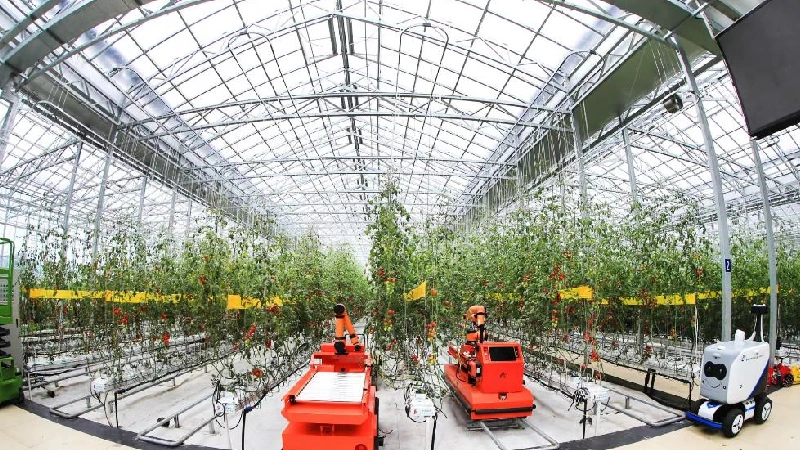

The core of an intelligent greenhouse includes a signal collection system that gathers data, a central computer that processes this information, and a control system that adjusts the environment based on real-time data and pre-set parameters. These systems work together to ensure optimal growth conditions and efficient resource use.
Read More: 10 Advantages of A Commercial Smart Greenhouse
5)Double-Layer Inflatable Film Greenhouses
As an advanced form of plastic film greenhouses, double-layer inflatable film greenhouses offer superior insulation and energy efficiency. By using two layers of polyethylene film with an inflated air gap in between, these structures can reduce energy loss by over 40% compared to traditional single-layer designs.
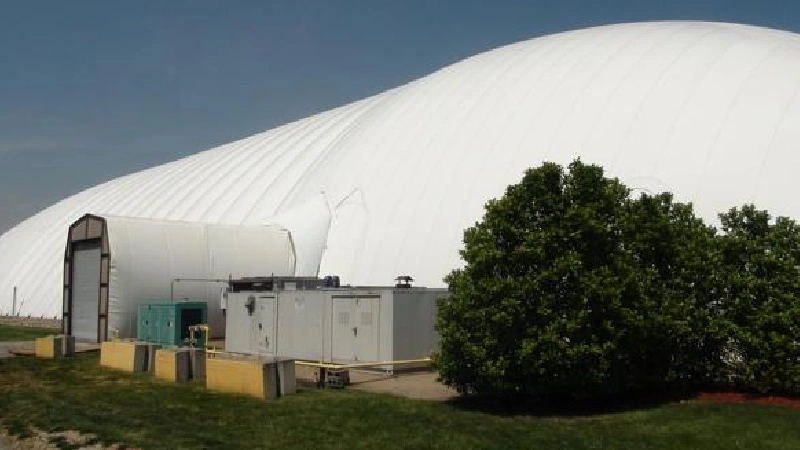

Structurally, they share the same base framework as standard plastic greenhouses but differ in film installation: instead of pressing the film directly onto the frame, the edges are sealed, and air is pumped between the two layers. This inflation not only improves structural rigidity but also creates a thermal barrier that minimizes heat loss and condensation. Double-layer greenhouses are especially effective in cold climates or in projects aiming to reduce energy costs.
Conclusion
Commercial greenhouses play a key role in modern agriculture, combining human creativity and advanced technology with nature. As science and technology progress and people’s needs change, the variety of commercial greenhouses keeps increasing. We’ve looked at greenhouses from five main angles – purpose, structure, roof type, covering material, and tech upgrades – and identified 18 different types, helping you choose the best one for your needs.
Building commercial greenhouses involves many components and systems. If you’re considering starting in greenhouse agriculture, feel free to contact us anytime for more information about the construction process and current prices.





